| Glycemic Index | Glycemic Load |
115.0
|
89.2
|
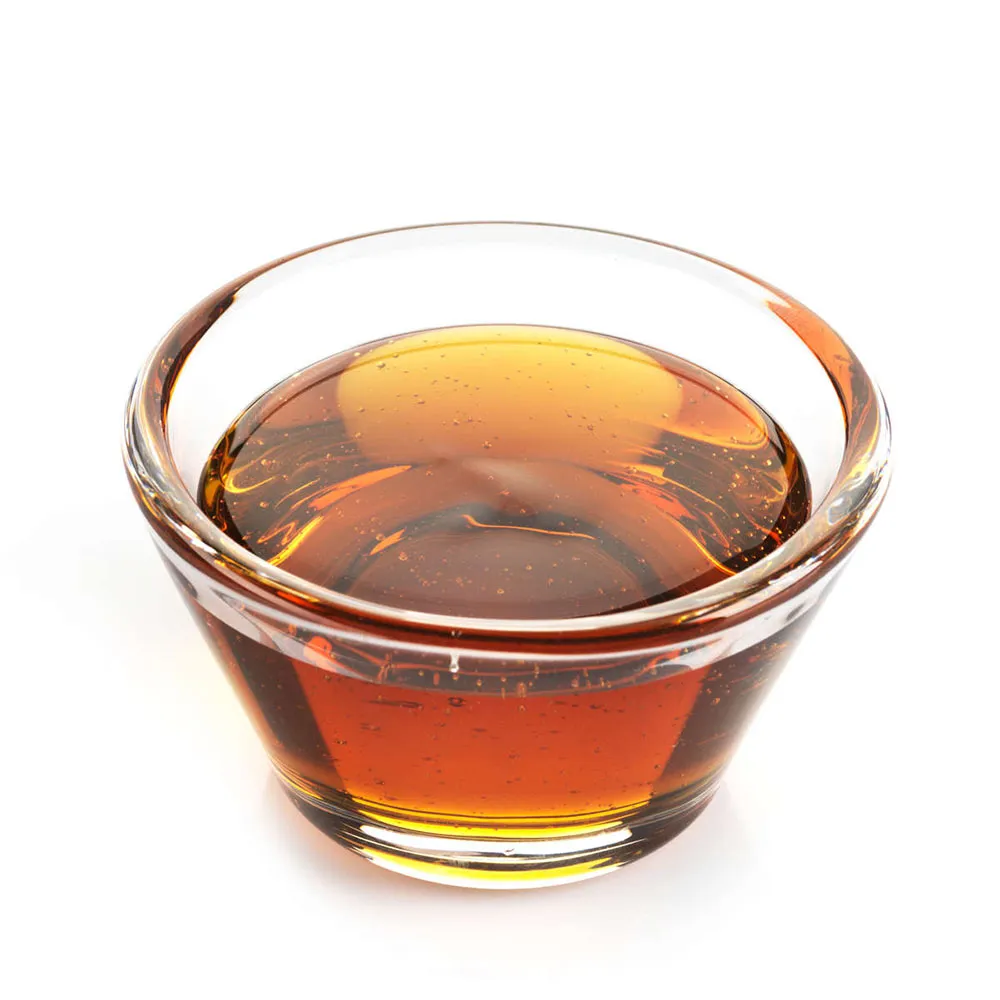
The glycemic index (GI) of corn syrup (dark) equals to 115.0, which classifies it as a high GI food. The glycemic load (GL) of corn syrup (dark) is equal to 89.2, which classifies it as a high GL food.
| Nutrition Facts | |
| Calories (kcal) | 286.0 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 77.6 |
| Proteins (g) | 0.0 |
| Fats (g) | 0.0 |
100 grams of corn syrup (dark) contain 286.0 kcal (1197 kJ), 0.0 grams of proteins, 77.6 grams of carbohydrates, and 0.0 grams of fats.
Corn syrup (dark) is a sweetener made from corn starch. It has a distinctive dark color and thick texture. Nutritionally, it contains no fat or protein but does provide carbohydrates in the form of simple sugars like glucose and dextrose. Dark corn syrup also provides some essential vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and potassium. One advantage to using dark corn syrup is that its sweetness level can be adjusted by adding other ingredients like molasses or honey for additional flavor complexity. The dark variety also tends to have greater depth of flavor than light versions due to the added natural flavors which are usually caramelized sugar products with added spices such as cinnamon or vanilla extract. Additionally, because it has a thick consistency compared with liquid alternatives like agave nectar or maple syrup, it may work better in certain recipes where viscosity matters more than sweetness levels alone such as baked goods or sauces/glazes used on meats or vegetables that require thicker coatings after cooking. On the downside though, since this type of product depends heavily upon high fructose sources they should generally be consumed in moderation since these types of sugars can upset blood sugar balance when eaten too often over time. Additionally there are concerns about potential links between HFCS consumption & increased risk for metabolic diseases although research continues into this area at present.