| Glycemic Index | Glycemic Load |
80
|
17.2
|
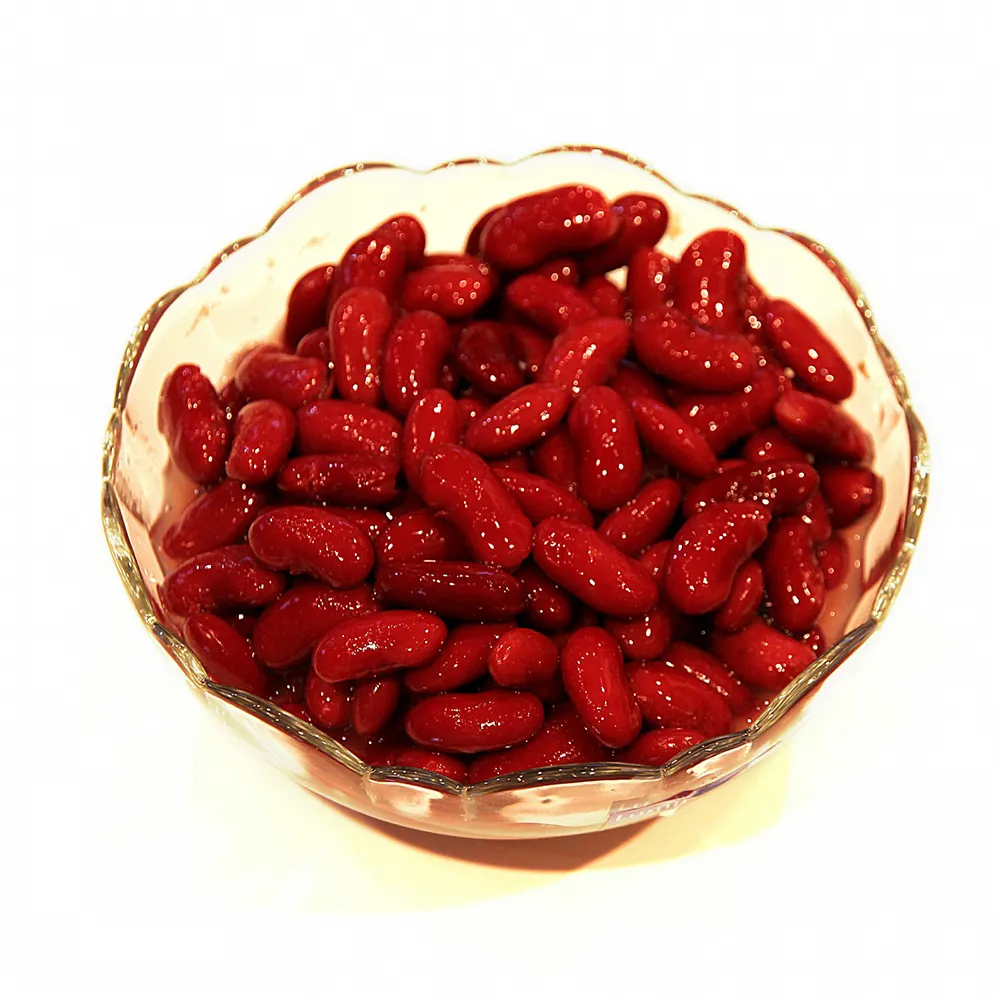
The glycemic index (GI) of beans (cooked) equals to 80, which classifies it as a high GI food. The glycemic load (GL) of beans (cooked) is equal to 17.2, which classifies it as a moderate GL food.
| Nutrition Facts | |
| Calories (kcal) | 123 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 21.5 |
| Proteins (g) | 7.8 |
| Fats (g) | 0.5 |
100 grams of beans (cooked) contain 123 kcal (515 kJ), 7.8 grams of proteins, 21.5 grams of carbohydrates, and 0.5 grams of fats.
Beans (cooked) are a great source of nutrition, providing protein, fiber and many other vitamins and minerals. They are low in fat and calories but high in complex carbohydrates which provide sustained energy throughout the day. One cup of cooked beans contains around 15 grams of dietary fiber, making them beneficial for digestive health. Fiber also helps to manage blood sugar levels by slowing down digestion and absorption rate into the bloodstream. Additionally they contain essential nutrients such as iron, magnesium, phosphorous and potassium that help regulate bodily functions like metabolism or muscle contractions. The main benefits associated with eating beans is their ability to reduce cholesterol levels due to their rich content of soluble fibers known as beta-glucans found within them; this results in improved cardiovascular health over time if eaten regularly enough. Furthermore they can aid weight loss since they’re so filling yet low calorie – you’ll feel full after just one serving! On the downside however some people find cooked beans hard to digest because some types contain difficult-to-digest sugars called oligosaccharides – cooking them properly before consumption may help with this issue though! Eating too much could lead to uncomfortable bloating or flatulence too due its high fibre content; moderation is key here when it comes down to how much we eat at once!